Virtuoso Authentication Layer (VAL) Installation and Configuration Guide
Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- VAL VAD Installation
- Setup Virtuoso HTTPS Listener
- VAL Configuration
- Setup VAL OpenID Connect Authentication
- Setup Access Controls
- Troubleshooting
- Related Resources
Prerequisites
- Latest Virtuoso 7.2.x or 8.x commercial edition
- Latest VAL VAD package
- Configure virtuoso.ini:
[Flags]section: Setenable_g_in_sec = 1(Virtuoso 8.x only)[URIQA]section: SetDefaultHostto canonical host/domain name
- Setup secure HTTPS access via reverse proxy or built-in HTTPS Listener
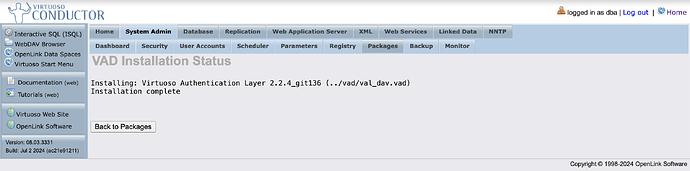
VAL VAD Installation
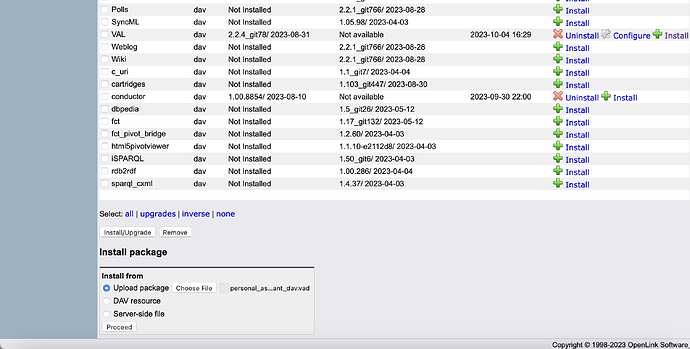
Install via Conductor interface:
- Navigate to System Admin → Packages
- Option 1: Install from vad/ directory
- Select VAL VAD from list
- Click Install/Upgrade
- Option 2: Manual installation
- Scroll to Install package → Install from
- Click Choose File
- Navigate to downloaded VAD
- Click Proceed
Setup Virtuoso HTTPS Listener
VAL requires secure HTTPS for OIDC authentication, which can be setup with one of two options:
Reverse Proxy Server HTTP Listener
- Handles SSL HTTP encryption
- Common Reverse Proxy Server options: Nginx, Apache, HAProxy, Squid
- Cloud providers often have custom solutions
Virtuoso built-in HTTPS Listener
- Built-in secure HTTP support
- Configure per Virtuoso HTTPS Listener documentation
- Follow VAL endpoint configuration guide
Virtuoso Authentication Layer (VAL) Configuration
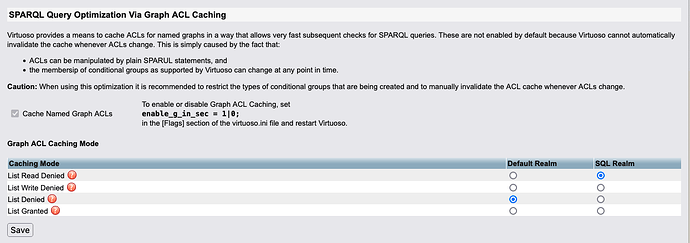
ABAC ACLs and Graph Caching
Enable Graph Caching Mode for scalable Attributed-Based Access Control:
- Edit virtuoso.ini:
[Flags]
enable_g_in_sec = 1
- Enable via Conductor UI:
- System Admin → Packages
- Select VAL configure link
- Check “Cache Named Graph ACLs”
- Or via isql:
__dbf_set('enable_g_in_sec',1)
Setup VAL OpenID Connect (OIDC) Authentication
VAL enables a Virtuoso Instance to function as an OpenID Connect (OIDC) or OAuth Relying Party or function as the Identity Provider (IdP). OIDC and OAuth Protocols are supported, alongside other protocols including TLS, WebID-TLS, WebID-OIDC, Digest Authentication, and OpenID.
The OpenID Connect (OIDC) and OAuth Protocol Virtualization details how VAL can be setup for OIDC authentication against remote 3rd party Identity Providers like Google, Microsoft, Apple, LinkedIn and any OIDC compliant 3rd party IdP.
Setup Access Controls
Service IDs
VAL enforces data access policies based on ServiceIDs that uniquely identify resource requestors. ServiceIDs can be:
- NetID: URI from third-party authentication services (e.g.,
https://plus.google.com/+JohnSmith) - WebID: Resolvable URI in X.509 certificate SubjectAlternativeName
Query the current user’s ServiceID:
SELECT bif:connection_get ('NetId') {}
Realms
ACL rules and groups are defined in application realms stored with oplacl:hasRealm. Key realms:
oplacl:DefaultRealm: Default realm for SPARQL clientsoplacl:SqlRealm: For SQL clients (ODBC, JDBC, etc.)
Rules
ACL rules grant permissions to ServiceIDs directly or through groups via acl:agent. Example rule:
@prefix oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
@prefix acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
<#rule>
a acl:Authorization;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Read;
acl:agent <http://www.facebook.com/jsmith>;
acl:accessTo <http://www.fusepool.eu/p3/assets>;
oplacl:hasScope <urn:myscope>.
Rules are stored in realm-specific graphs. Each permission must be explicitly stated.
Groups
Groups can be:
- Simple lists of members
- Conditional groups with attribute tests
- Public access via
acl:agentClass foaf:Agent
Groups are stored in realm-specific graphs. Conditional groups enable Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC).
Scopes
Scopes identify protected resource types and enable/disable ACL checking. Standard scopes include:
- Query:
oplacl:Query - Private graphs:
oplacl:PrivateGraphs - Entity description:
urn:virtuoso:val:scopes:sponger:describe - About endpoint:
urn:virtuoso:val:scopes:sponger:about - Sponger cartridges:
oplacl:SpongerCartridges
Enable scopes via Conductor UI or directly:
SPARQL PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:config>
DELETE { oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasDisabledAclScope oplacl:Query }
INSERT { oplacl:DefaultRealm oplacl:hasEnabledAclScope oplacl:Query };
Troubleshooting
- Enable OAuth2 debugging:
registry_set ('__debug_oauth2.0', '1')
- Check ServiceID:
SELECT bif:connection_get ('NetId') {}
- Verify ACL graph IRIs:
SELECT VAL.DBA.val_acl_group_graph(VAL.DBA.get_default_realm());
SELECT VAL.DBA.val_acl_rule_graph(VAL.DBA.get_default_realm());
SELECT VAL.DBA.val_restrictions_graph(VAL.DBA.get_default_realm());
Use PL Debugger for detailed session inspection:
- Connect via isql -D
- Set breakpoint:
break ws.ws./!sparql/ - Check threads:
info threads - Attach to HTTP thread
- View globals
- Detach and continue