This installation guide walks you through the installation of the Lite Edition ODBC Driver for Microsoft SQL Server to a Personal or Application Server host functioning as a client to a SQL Server Database.
Step 1: Download the Installer Archive
- Visit the OpenLink ODBC Lite Edition Driver Download Page to download the appropriate ODBC driver for SQL Server.
- Alternatively,
curlcan be used to download the installer directly.
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/10.0/universal-apple-macos11-64/m1l10mzzz.dmg
Installation
- Run the
m1l10mzzz.dmgmacOS DMG installer disk image file.
- Double click on the
OpenLink-SQLSever-Lite.pkginstaller package
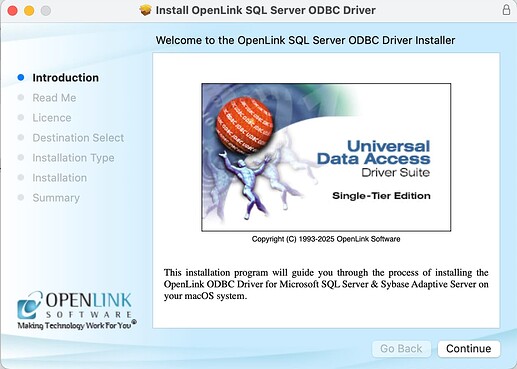
- Select the
Continuebutton to proceed with the installation.
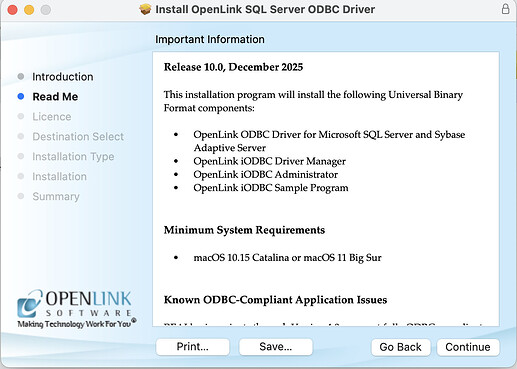
- Select the
Continuebutton to proceed orPrintorSaveto save theRead Medocument.
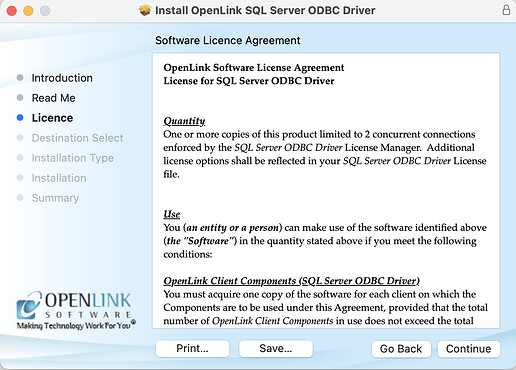
- Select the
Continuebutton to proceed orPrintorSaveto save theLicenseagreement.
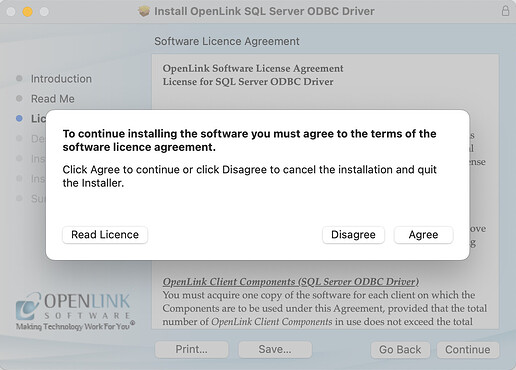
- Select
Agreeto accept the license agreement.
- Choose which components to install, default are recommend, and click the
Continuebutton to proceed.
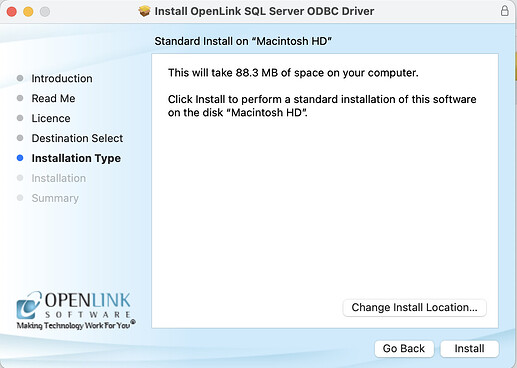
- Choose the
Installbutton to install the driver in the default recommended location.
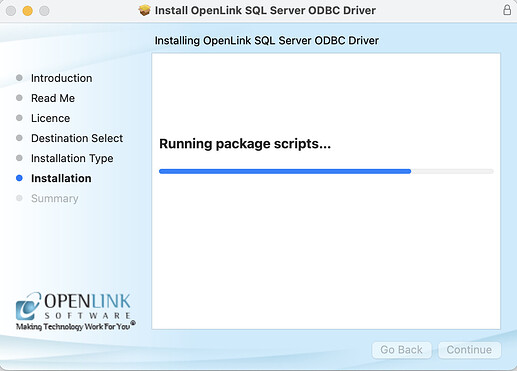
- The installation is in progress.
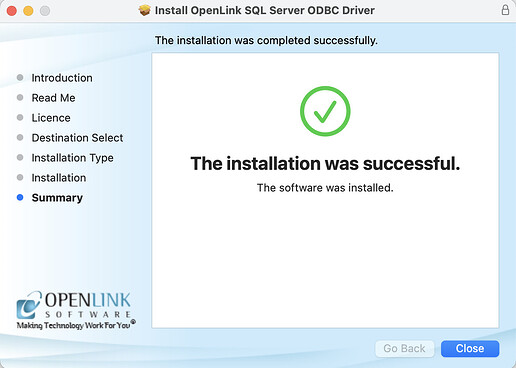
- The installation is completed successfully.
Move to BinorKeepthe installer package.
Configuration
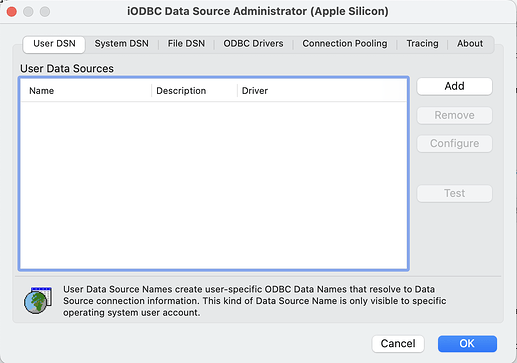
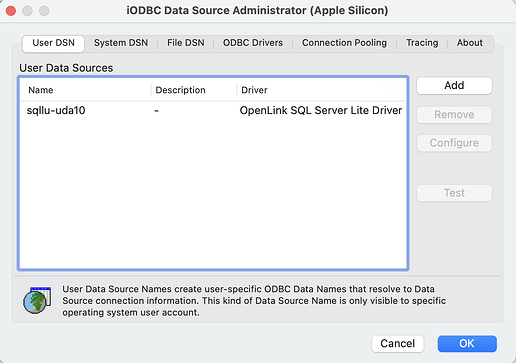
- Open the macOS
iODBC Administratorin the/Application/iODBCfolder.
- Click on the
Addbutton to create an ODBC DSN.
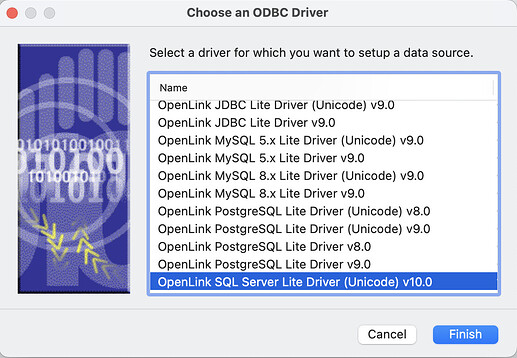
- Select the
OpenLink SQL Server Driver (Unicode) v10.0ODBC driver.
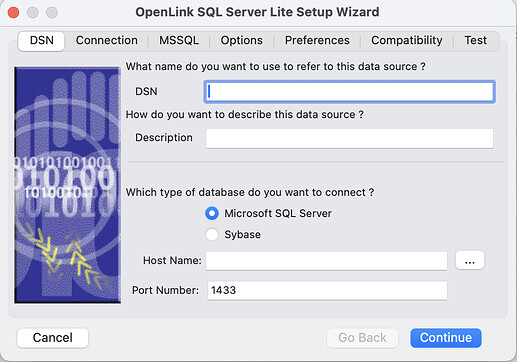
- Enter an ODBC DSN
name, chooseMicrosoft SQL Serveras the database type and enter theHost NameandPortnumber of the target SQL Server instance…
- Host Name - The hostname or IP address on which Microsoft SQL Server listens
- Port - The TCP port on which Microsoft SQL Server lists
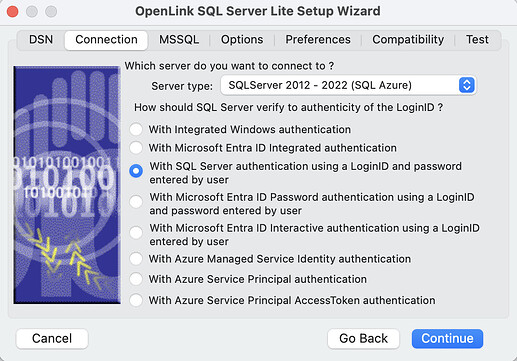
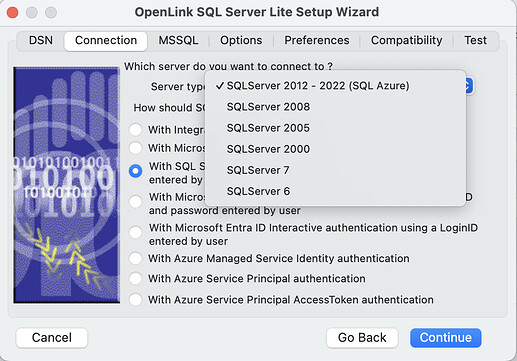
- Choose the SQL Server authentication method to be used.
Authentication Methods:
- With Integrated Windows authentication (ntlm) - Specifies that the driver request a secure (or trusted) connection to a SQL Server. When selected, SQL Server uses integrated login security to establish connections using this data source, regardless of the current login security mode at the server. Any login ID or password supplied is ignored. The SQL Server system administrator must have associated your Windows login with a SQL Server login ID (for example, by using SQL Server Management Studio).
- With Microsoft EntraID Integrated authentication (ActiveDirectoryIntegrated) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using Microsoft Entra ID. When selected, SQL Server uses Microsoft Entra integrated login security to establish a connection using this data source, regardless of the current login security mode at the server.
- With SQL Server authentication using a LoginID and password entered by user (Default) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using a login ID and password.
- With Microsoft EntraID Password authentication using a LoginID and password entered by user (ActiveDirectoryPassword) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using a Microsoft Entra login ID and password.
- With Microsoft EntraID Interactive authentication using a LoginID and password entered by user (ActiveDirectoryInteractive) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using Microsoft Entra interactive mode by providing a login ID. This option triggers the Azure Authentication prompt dialog.
- With Azure Managed Service Identity authentication (ActiveDirectoryMsi) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using a Managed Identity.
- With Azure Service Principal authentication (ActiveDirectoryServicePrincipal) - Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using a Microsoft Entra service principal.
- With Azure Service Principal AccessToken authentication (ActiveDirectoryServicePrincipalAccessToken) - Specify your own code for generating an AccessToken from Azure server , which can be passed as the Password with a
blankUsername for connection to the database. The Azure CLI commandaz account get-access-token --resource https://database.windows.net/can be used to generate an AccessToken.
- Choose the SQL
Server Typeto be connected to.
- Server Type - An OpenLink proprietary parameter that associates the connection with a particular TDS version.
- Enter the
Instance Name,Mirror Host,Conn Timeout,Multi Subnet Failover,Use string encryption for dataas or if applicable. Then select theConnect now to verify that all settings are correctoption and provide login details, then clickNextto validate a connection can be made.
- Instance Name - Microsoft SQL Server instance name on the specified host. A Microsoft SQL Server instance can also be specified by appending
\InstanceNameto the ServerName ieServerName\InstanceName - Mirror Host - The name of the Failover Server hosting the mirrored database if configured
- Conn Timeout - Connection timeout in
msec. - Multi Subnet Failover - This flag switches
ONSQL Server Multi Subnet Failover mode - Use strong encryption of data - Enable SSL encryption of data between driver and database
- Connect now to verify that all settings are correct - Will attempt to connect to the database, once you click Continue.
- Login ID - A valid Microsoft SQL Server username
- Password - A valid Microsoft SQL Server password
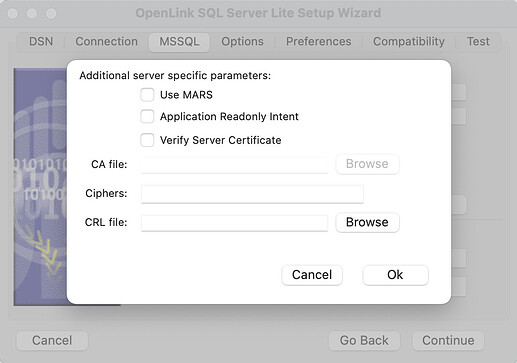
- Use the Advanced button to configure advance connection attributes if required, as detailed below.
- Use Mars - Multiple Active Result Sets enables the concurrent processing of multiple statements/queries and/or result sets on a single connection
- Application Readonly Intent - Application Intent is applicable to SQL Server clustered instances, and is a request for the driver to ask the SQL Server listener for connectivity to either a
read onlyorread writenode within the cluster. The driver has no control over the routing as it is the responsibility of the SQL Server listener to route the connection to one of the nodes in the Availability Group. The default isread writeand this option allows it to be toggled toread only. - Verify Server Certificate - Verify the Database Server SSL certificate against the one specified in the “CA file” field
- CA file - Specify the location of a Valid SSL Certificate for use during the connection
- Ciphers - List of encryption algorithms used to protect data in transit
- CRL file - A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) file containing a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the CA (Certificate Authority) before their scheduled expiration date
- Enter the
Database,Character setandLanguageor select from available items in the drop down list boxes and clickNext.
- Database - The Microsoft SQL Server database
- Character set - The client application’s character set (8-bit only; the Unicode driver always returns UCS-2 on Windows).
- Language - The language you want error messages returned in; must be supported by the target server.
- Packet Size - A value that determines the number of bytes per network packet transferred from the database server to the client. The correct setting of this attribute can improve performance. When set to 0, the initial default, the driver uses the default packet size as specified in the Microsoft SQL Server configuration. When set to -1, the driver computes the maximum allowable packet size on the first connect to the data source and saves the value in the system information. When set to x, an integer from 1 to 10, which indicates a multiple of 512 bytes (for example, Packet Size of 6 means to set the packet size to 6 * 512 equal 3072 bytes). For you to take advantage of this connection attribute, you must configure the System 10 server for a maximum network packet size greater than or equal to the value you specified for Packet Size.
- Prepare Method - This option is specific to the TDS-based driver for Sybase & Microsoft SQL Server SQL Servers. It can take the values None, Partial, or Full (
connectoptions = -O [0, 1, 2]respectively). It is used to determine whether stored procedures are created on the server for calls to SQLPrepare. More - No Quoted Identifiers - This option indicates that the underlying driver does not support quoted identifiers, which is required for Jet engine based products like MS Access.
- Use ANSI nulls, padding and warnings - This option affects TDS agent & Lite Driver connections to Microsoft SQL Server databases. Sybase connectivity is not affected. More
- Map Serializable to Snapshot isolation level - Enable Snapshot transaction isolation level in the driver. Snapshot Isolation is a new transaction isolation level available in Microsoft SQL Server 2005
- Show Sparse Columns in SQLColumns - Display SQL Server Sparse Columns in ODBC
SQLColumnscall.
- These parameters can typically as defaults and click
Next.
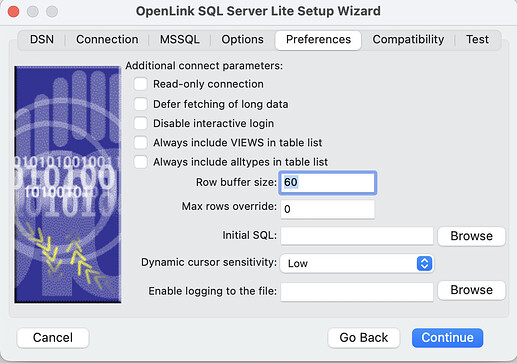
- Read-only connection — Specifies whether the connection is “Read-only.” Must be unchecked to INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE records, and to run some Stored Procedures including some built-in functions.
- Defer fetching of long data — Defers fetching of LONG (BINARY, BLOB, etc.) fields in wildcard queries. This provides significant performance increases when fields in query do not include LONG data fields.
- Disable interactive login — Suppresses the ODBC “Username” and “Password” login dialog boxes when interacting with your ODBC DSN from within an ODBC compliant application.
- Row Buffer Size — This attribute specifies the number of records to be delivered from the driver to the client application in a single batch. Values can range from 1 to 999.
- Max Rows Override — Allows you to set a limit for the maximum number of rows to be returned from a query. The default value of 0 means no limit.
- Initial SQL — Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
- Dynamic Cursor Sensitivity — Enables or disables the row version cache used with dynamic cursors. When dynamic cursor sensitivity is set high, the Cursor Library calculates checksums for each row in the current rowset and compares these with the checksums (if any) already stored in the row version cache for the same rows when fetched previously. If the checksums differ for a row, the row has been updated since it was last fetched and the row status flag is set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED. The row version cache is then updated with the latest checksums for the rowset. From the user’s point of view, the only visible difference between the two sensitivity settings is that a row status flag can never be set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED when the cursor sensitivity is low. (The row status is instead displayed as SQL_ROW_SUCCESS.) In all other respects, performance aside, the two settings are the same. Deleted rows don’t appear in the rowset. Updates to the row since the row was last fetched are reflected in the row data, and inserted rows appear in the rowset, if their keys fall within the span of the rowset. If your application does not need to detect the row status SQL_ROW_UPDATED, you should leave the High Cursor Sensitivity checkbox unchecked, as performance is improved. The calculation and comparison of checksums for each row fetched carries an overhead. If this option is enabled, the table oplrvc must have been created beforehand using the appropriate script for the target database.
- Enable logging to the log file — Check the checkbox and use the associated textbox to provide the full path to a file in which to log diagnostic information.
- These parameters can typically as defaults and click
Next.
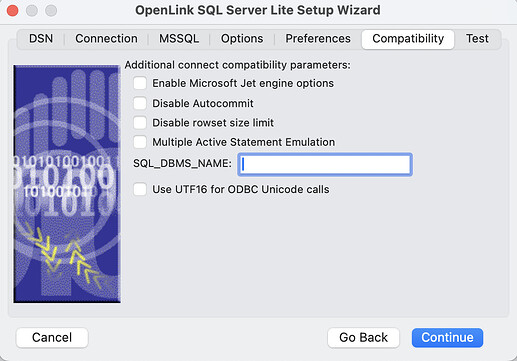
- Enable Microsoft Jet engine options — Facilitates translation of certain data types for the Microsoft Jet Engine. If you notice that money and other datatypes are mishandled with Microsoft or other applications, test with Jet fix enabled.
- Disable Autocommit — Changes the commit behavior of the OpenLink driver. The default mode is AutoCommit (box unchecked).
- Disable rowset size limit — Disables a limitation enforced by the cursor library. This limitation is enforced by default. It prevents the driver from claiming all available memory when a resultset (typically generated by an accidental query) is very large. The limit is not normally reached.
- Multiple Active Statements Emulation — Enables use of Multiple Active statements in an ODBC application even if the underlying database does not allow this, by emulation within the driver.
- SQL_DBMS_NAME — Manually overrides the SQLGetInfo(SQL_DBMS_NAME) response returned by the driver. This is required for products like Microsoft InfoPath for which the value should be “SQL Server”.
- Use UTF16 for ODBC Unicode calls - When using the unixODBC Driver Manager, this parameter needs to be set to enable successful connections with applications built using the unixODBC SDK.
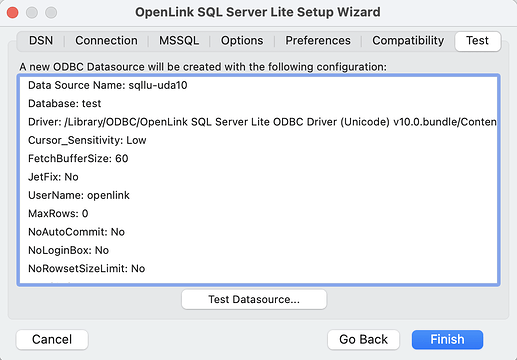
- Select the
Test Data Sourcebutton to make a test connection to the database.
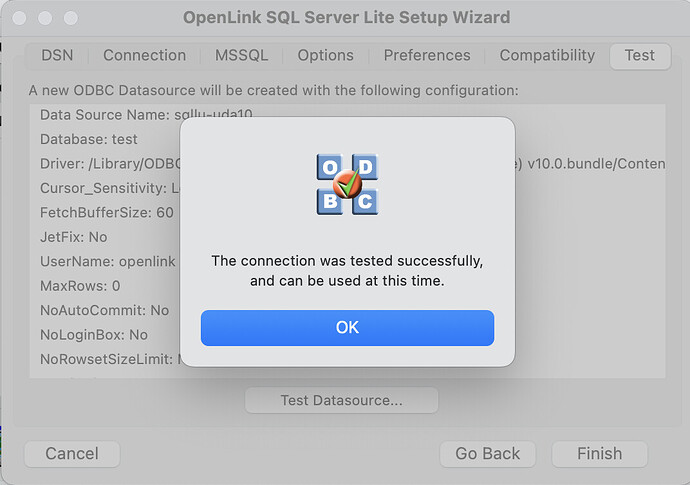
- The test connection was successful.
- The DSN is successfully added and ready for use.
C++Demo test connection
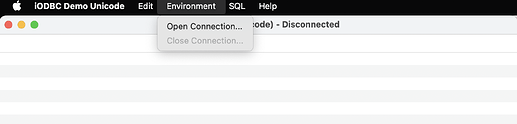
- From the
/Applications/iODBCfolder run theiODBC Demo Unicodesample application.
- Select the
Environment -> Open Connectionmenu item.
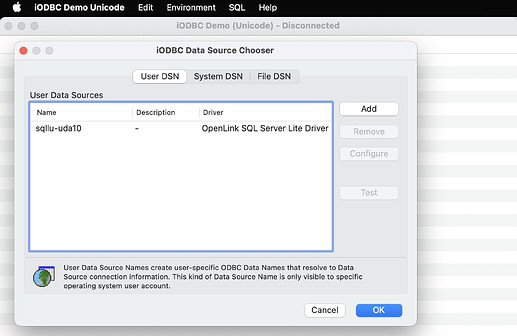
- Select the ODBC DSN to use.
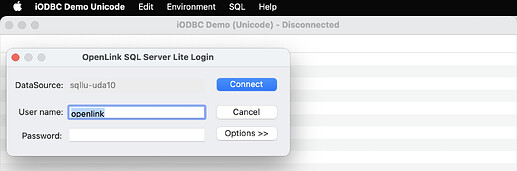
- Enter login details for the target database.
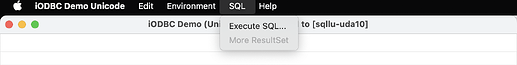
- Select the
SQL -> Execute SQLmenu item.
- Enter a valid SQL query and click the ‘OK’ button to run it.
- The query results are displayed.