NetID-TLS Client Certificate Authentication Protocol Explainer (Revised Edition)
CHAT-GPT Transcript
NetID-TLS CCA extends the basic protocol by adding the following steps immediately after step 6:
- Locate Identifier value in the client certificates Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field
- Lookup (de-reference) Identifier to its associated Profile Graph (which can exist in a variety of forms including metadata embedded in an HTML based Link In Bio Page)
- Find at least one of the following in the Profile Graph: Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key
Q: Describe NetID-TLS CCA
A:
NetID-TLS CCA (Client Certificate Authentication) is an extended TLS authentication protocol that adds extra steps to locate an identifier in the client certificate and de-reference it to an associated Profile Graph. Here’s a step-by-step guide for the NetID-TLS CCA authentication sequence:
-
Establish a connection: The client initiates a connection to the server by sending a “ClientHello” message, which includes the highest TLS version supported by the client, a list of supported cipher suites, and other extensions.
-
Server response: The server responds with a “ServerHello” message, selecting a mutually supported TLS version and cipher suite. The server also sends its digital certificate, which contains its public key and information about the server’s identity, signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
-
Request for client certificate: If the server requires CCA, it sends a “CertificateRequest” message to the client. This message may include a list of acceptable CAs that the server trusts to issue client certificates.
-
Client certificate: If the client has a certificate issued by one of the acceptable CAs, it sends the certificate to the server in a “Certificate” message. If the client doesn’t have a suitable certificate or chooses not to send it, it can send an empty “Certificate” message or a “no_certificate” alert.
-
Client key exchange and authentication: The client generates a pre-master secret and encrypts it with the server’s public key, then sends it to the server in a “ClientKeyExchange” message. The client also signs a piece of data derived from the handshake messages using its private key, and sends the signature in a “CertificateVerify” message, which allows the server to authenticate the client.
-
Server authentication and key derivation: The server decrypts the pre-master secret using its private key and authenticates the client by verifying the signature in the “CertificateVerify” message. Both the client and the server derive a master secret from the pre-master secret and use it to generate symmetric encryption keys and MAC keys.
-
Locate Identifier value: In the NetID-TLS CCA extension, the server locates the Identifier value in the client certificate’s Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field.
-
Lookup (de-reference) Identifier: The server looks up the Identifier to its associated Profile Graph, which can exist in various forms, such as metadata embedded in an HTML-based Link In Bio Page.
-
Find Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key: The server verifies the client’s identity by finding at least one of the following in the Profile Graph: Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key.
-
Secure communication: The client and the server exchange “ChangeCipherSpec” messages, indicating that they will start using the symmetric encryption keys and MAC keys derived from the master secret. They then exchange “Finished” messages to confirm that the handshake has been successful. From this point on, the client and server can securely communicate using the established encryption and integrity protection.
-
Connection termination: The client and server can exchange application data securely until either side decides to close the connection. A “close_notify” alert is sent by the party initiating the closure, and the other party responds with its own “close_notify” alert to confirm the connection termination.
Q: Redo using Mermaid Sequence notation.
A:
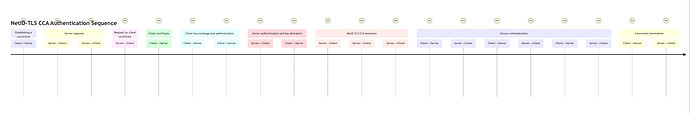
journey
title NetID-TLS CCA Authentication Sequence
section Establishing a connection
Client-->Server: ClientHello
section Server response
Server-->Client: ServerHello
Server-->Client: Server Certificate
section Request for client certificate
Server-->Client: CertificateRequest
section Client certificate
Client-->Server: Client Certificate (or empty/no_certificate)
section Client key exchange and authentication
Client-->Server: ClientKeyExchange
Client-->Server: CertificateVerify
section Server authentication and key derivation
Server-->Client: (Derive keys from pre-master secret)
Client-->Server: (Derive keys from pre-master secret)
section NetID-TLS CCA extension
Server-->Client: (Locate Identifier value in SAN)
Server-->Client: (Lookup Identifier to associated Profile Graph)
Server-->Client: (Find Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key in Profile Graph)
section Secure communication
Client-->Server: ChangeCipherSpec
Server-->Client: ChangeCipherSpec
Client-->Server: Finished
Server-->Client: Finished
Client-->Server: (Encrypted application data)
Server-->Client: (Encrypted application data)
section Connection termination
Client-->Server: close_notify (or vice versa)
Server-->Client: close_notify (or vice versa)
Mermaid User Journey Diagram
Here’s the live Mermaid User Journey diagram.
Q: Redo, using Mermaid Sequence notation.
A:
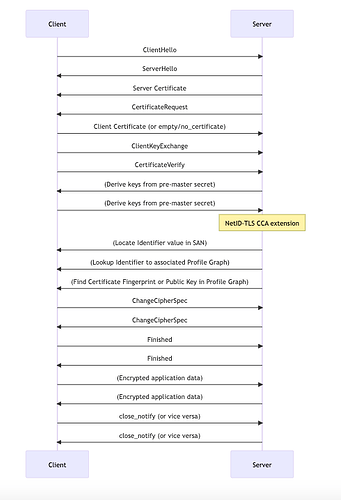
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant Server
Client->>Server: ClientHello
Server->>Client: ServerHello
Server->>Client: Server Certificate
Server->>Client: CertificateRequest
Client->>Server: Client Certificate (or empty/no_certificate)
Client->>Server: ClientKeyExchange
Client->>Server: CertificateVerify
Server->>Client: (Derive keys from pre-master secret)
Client->>Server: (Derive keys from pre-master secret)
Note over Server: NetID-TLS CCA extension
Server->>Client: (Locate Identifier value in SAN)
Server->>Client: (Lookup Identifier to associated Profile Graph)
Server->>Client: (Find Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key in Profile Graph)
Client->>Server: ChangeCipherSpec
Server->>Client: ChangeCipherSpec
Client->>Server: Finished
Server->>Client: Finished
Client->>Server: (Encrypted application data)
Server->>Client: (Encrypted application data)
Client->>Server: close_notify (or vice versa)
Server->>Client: close_notify (or vice versa)
Mermaid Sequence Diagram
Here’s a live Link to the Mermaid Sequence Diagram.
Q: Redo, but presenting the guide in a code-block comprising a Markdown Table.
A:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Establish a connection: The client initiates a connection by sending a “ClientHello” message to the server. |
| 2 | Server response: The server sends a “ServerHello” message, selects a cipher suite and sends its digital certificate. |
| 3 | Request for client certificate: The server sends a “CertificateRequest” message to the client. |
| 4 | Client certificate: The client sends its certificate to the server or an empty “Certificate” message. |
| 5 | Client key exchange and authentication: The client sends “ClientKeyExchange” and “CertificateVerify” messages. |
| 6 | Server authentication and key derivation: The server decrypts the pre-master secret and derives symmetric keys. |
| 7 | Locate Identifier value: The server locates the Identifier value in the client certificate’s SAN field. |
| 8 | Lookup (de-reference) Identifier: The server looks up the Identifier to its associated Profile Graph. |
| 9 | Find Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key: The server verifies the client’s identity using the Profile Graph. |
| 10 | Secure communication: The client and server exchange “ChangeCipherSpec” and “Finished” messages to secure the channel. |
| 11 | Connection termination: The client and server exchange “close_notify” alerts to close the connection. |
Q:
Redo, but using RDF-Turtle rendition in HowTo and Step-By Guide form, in line with these guidelines:
- place code within
## Turtle Start ##and## Turtle End ##block - use terms from Schema.org
- ensure each step is named via a schema:name attribute
- use schema:position and schema:nextItem for enhanced indexing and flow
- relative hash-based IRIs ( e.g., <#> ) for subject and object denotation
- include DBpedia cross-references where such exist, bearing in mind this is about pki, tls, https, cryptography, privacy, email, identity, and privacy pegged to the schema:HowTo instance description
A:
## Turtle Start ##
@prefix schema: <http://schema.org/> .
@prefix dbpedia: <http://dbpedia.org/resource/> .
@prefix : <#> .
:HowToNetID-TLS_CCA
a schema:HowTo ;
schema:name "NetID-TLS CCA Authentication Sequence" ;
schema:step :Step1 ;
schema:about dbpedia:Transport_Layer_Security,
dbpedia:Public_key_infrastructure,
dbpedia:HTTPS,
dbpedia:Cryptography,
dbpedia:Privacy,
dbpedia:Email,
dbpedia:Digital_identity .
:Step1
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Establish a connection" ;
schema:text "The client initiates a connection by sending a 'ClientHello' message to the server." ;
schema:position 1 ;
schema:nextItem :Step2 .
:Step2
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Server response" ;
schema:text "The server sends a 'ServerHello' message, selects a cipher suite and sends its digital certificate." ;
schema:position 2 ;
schema:nextItem :Step3 .
:Step3
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Request for client certificate" ;
schema:text "The server sends a 'CertificateRequest' message to the client." ;
schema:position 3 ;
schema:nextItem :Step4 .
:Step4
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Client certificate" ;
schema:text "The client sends its certificate to the server or an empty 'Certificate' message." ;
schema:position 4 ;
schema:nextItem :Step5 .
:Step5
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Client key exchange and authentication" ;
schema:text "The client sends 'ClientKeyExchange' and 'CertificateVerify' messages." ;
schema:position 5 ;
schema:nextItem :Step6 .
:Step6
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Server authentication and key derivation" ;
schema:text "The server decrypts the pre-master secret and derives symmetric keys." ;
schema:position 6 ;
schema:nextItem :Step7 .
:Step7
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Locate Identifier value" ;
schema:text "The server locates the Identifier value in the client certificate's SAN field." ;
schema:position 7 ;
schema:nextItem :Step8 .
:Step8
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Lookup (de-reference) Identifier" ;
schema:text "The server looks up the Identifier to its associated Profile Graph." ;
schema:position 8 ;
schema:nextItem :Step9 .
:Step9
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Find Certificate Fingerprint or Public Key" ;
schema:text "The server verifies the client's identity using the Profile Graph." ;
schema:position 9 ;
schema:nextItem :Step10 .
:Step10
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Secure communication" ;
schema:text "The client and server exchange 'ChangeCipherSpec' and 'Finished' messages to secure the channel." ;
schema:position 10 ;
schema:nextItem :Step11 .
:Step11
a schema:HowToStep ;
schema:name "Connection termination" ;
schema:text "The client and server exchange 'close_notify' alerts to close the connection." ;
schema:position 11 .
## Turtle End ##